Eg Of Thermal Energy

Science For Kids Heat Energy Video Youtube

12 Examples Of Thermal Energy In Everyday Life Rankred

Heat And Temperature By Ms Lyons Ppt Video Online Download
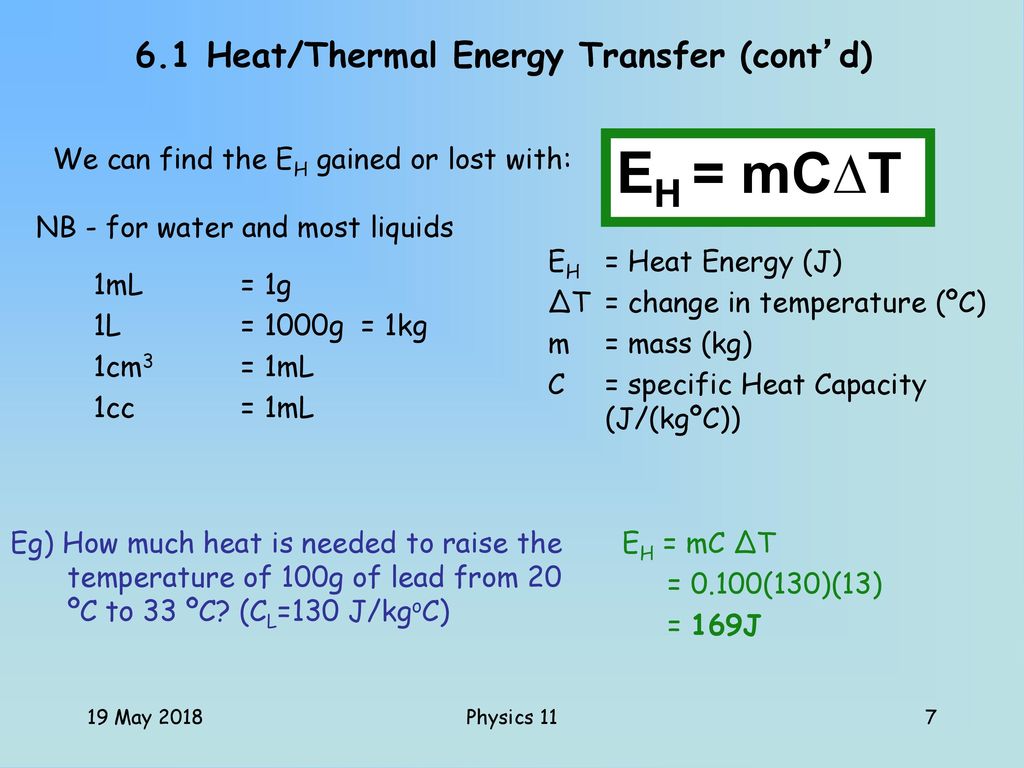
Heat Energy 19 May 18 Physics Ppt Download

What S The Difference Between Conduction Convection And Radiation Machine Design

Thermal Energy Storage Technologies And Systems For Concentrating Solar Power Plants Sciencedirect
The four selected PCM composites were composed of pentadecane and expanded graphite (EG), and achieved effective thermal conductivities (keff) of 0.21 W/ (m·K), 1 W/ (m·K), 8.6 W/ (m·K) and W/ (m·K)), respectively.

Eg of thermal energy. The transfer of thermal energy from one object or system to another. Examples of thermal energy. Hence the energy required to jump is around 0 times the energy at room temperature.
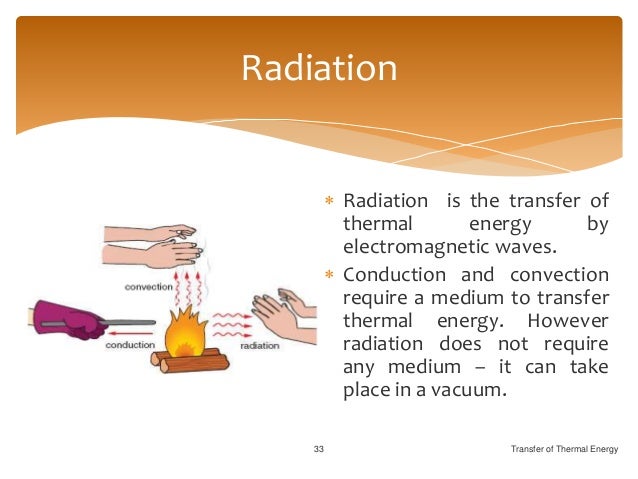
Thermal energy piping will connect at the existing valves located at the intersection of Magnolia Drive and 6th Street to provide hot and chilled water to the buildings which will allow for the decommissioning of the existing equipment. Radiation is the transfer of energy along electromagnetic waves, like light waves and radio waves. Productive Uses of Thermal Energy.
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact between. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. The sun is the main source of heat energy.
Sustainable Development Goal #7 is to “ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all” 1. These molecules move (or vibrate) constantly. Maintain components such as electronics and materials in allowable temperature ranges 3.
Thermal comfort in buildings, transports… 2. Last but not leas. Thermal Energy Transfer can occur by three methods:.
Electrical energy can be supplied easily to any desired place through wires. For example, thermal energy exists because of the movement of atoms or molecules, thus thermal energy is a variation of kinetic energy. These are the two basic forms of energy.
Thermal energy is an internal energy for a given system. Most of us refer the word ‘heat’ to anything that feels warm but scientifically, heat is defined as the flow of energy from a warm to a cooler object. Thermal Energy Thermal energy is the total energy of all of the particles in a substance.
All matter contains heat energy, and the more heat energy that is present, the hotter an item or area will be. Gasoline is burned in a car engine. When two systems (eg two beakers of water) are at the same temperature, we say they are in _____ _____.
The amount of expansion differs in solids, liquids, and gases. An object with molecules that are very "excited" and move around rapidly is known as being hot, while an object with molecules whose atoms move around less rapidly is known as cold. When a fire is applied to wood, the molecules in the wood fragments react with the oxygen (air).
In thermodynamics, thermal energy (also called the internal energy) is defined as the energy associated with microscopic forms of energy.It is an extensive quantity, it depends on the size of the system, or on the amount of substance it contains.The SI unit of thermal energy is the joule (J). Electricity other than photovoltaic 4. Thermal energy, which is more commonly known as heat, is a form of energy.
Thermal Energy and Temperature. Lauric acid/expanded graphite (LA/EG) composite phase change materials (PCMs) were prepared to collect and store solar energy as latent heat thermal energy. Gases expand the ….
The standard symbol for “change” is the Greek letter delta (∆), so the change in T is written ∆T. The signs of internal energy. Dry wood is a store of chemical energy.
One Btu is the amount of energy needed to raise a pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Heat is a form of energy. It is measured in joules.
Most of manufacturing processes (since bronze age) 5. Heat and heat energy are terms we use to describe the level of activity for the molecules in an object. Thermal Energy is energy resulting from the motion of particles;.
Heat is the flow of thermal energy. The potential energy of an object or system. The foods we take provide us heat energy.
Of the three methods of heat transfer, radiation is the only one that can travel through empty space. Thermal energy is one of various types of energy, where ' energy ' can be. Electricity is one of the widely used forms of energy.
A cup of hot coffee has thermal energy. Estimates of the temperature of the core range from. The chemical energy causes the liquid water molecules to move faster increasing their thermal energy.
This will also allow both buildings to be converted. As the gas burns, small explosions release heat or thermal energy which makes the pistons move so the car go. Ultraviolet‐visible spectra demonstrated that the ability of LA/EG composite PCMs to absorb Ultraviolet‐visible light would increase as the mass fraction of EG increases.
A unit of measure for the energy content of fuels. The earth's core lies almost 4,000 miles beneath the earth's surface. Geothermal energy is the thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth.
Internal Energy Change Equations. Of man-made materials can be included into the environmental equation to provide a wider environmental benefit eg where space for insulation is at a premium such as in retrofit. The energy that comes from the temperature of the heated substance is called thermal energy.
Thermal energy is produced by the heat that is given off from specific sources. The classification of heat is done on this basis as hot and cold. Heating makes the particles (that form the material) expand or become loose.
When a wave comes into contact with an object, the energy is transferred to the object in the form of heat. It is a form of kinetic energy and is transferred as heat;. When a system has a well-defined temperature, we know it is in _____ _____.
In this lab, we will focus on the ways heat is transferred. Similarly, the thermal energy input is the amount by which the thermal energy. Thermal energy or heat energy reflects the temperature difference between two systems.
KT (also written as k B T) is the product of the Boltzmann constant, k (or k B), and the temperature, T.This product is used in physics as a scale factor for energy values in molecular-scale systems (sometimes it is used as a unit of energy), as the rates and frequencies of many processes and phenomena depend not on their energy alone, but on the ratio of that energy and kT, that is, on E / kT. As it burns in the fireplace, chemical energy is released and converted to thermal energy (heat) and light energy. The faster the atoms are moving, the higher the temperature.
Particles of a substance, without moving the. Thermal energy is energy possessed by an object or system due to the movement of particles within the object or the system. Thermal energy, internal energy present in a system in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium by virtue of its temperature.Thermal energy cannot be converted to useful work as easily as the energy of systems that are not in states of thermodynamic equilibrium.A flowing fluid or a moving solid, for example, possesses energy that can be converted to work in some mechanical device, such as a.
The destruction of thermal energy in an object or system. This is how the Sun's heat can. The hotter the substance, the more its molecules vibrate, and therefore the higher its thermal energy.
Thermal energy refers to the energy contained within a system that is responsible for its temperature. Involve transfer of energy between a closed system and its' surroundings. Internal energy is the energy of.
One energy type that can contribute to this sustainable development goal is thermal energy – energy from the burning of biomass or solar energy – and it often gets overlooked by governments and donors because burning biomass can be. Now for an electron to jump to these higher unoccupied levels, it requires energy which is equal to Eg(forbidden gap energy). Choose from 500 different sets of thermal energy flashcards on Quizlet.
Figure 1.21 shows molecules in two bodies at different temperatures, T h T h and T c, T c, for “hot” and “cold.” The average kinetic energy of a molecule in the hot body is higher than in the colder body. It is a kind of kinetic energy that is produced when the molecules of a heat-emitting body or object, experience an acceleration in their velocity, or an increase in their molecular activities. In all materials, the atoms that make up their molecules are in continuous movement, either moving or vibrating.
Cooling makes the particles (that form the material) contract or become tight. The chemical energy released as the coal is burned heats water and turns it into steam. Thermal energy is directly proportional to the temperature within a given system (recall that a system is the subject of interest while the surroundings are located outside of the systems and the two interact via energy and matter exchange.) As a result of this relationship between thermal energy and the temperature of the system, the following applies:The more.
A rise in the temperature of matter makes the particles vibrate faster. The mixture of KCl-LiCl was served as the phase change material (PCM) for thermal energy storage, while EG was acted as not only the matrix to prevent the leakage of PCM but also. Where q is heat and w is work.
As such thermal energy can also be defined as the ability of something to do work as a result of the movement of its particles. Expansion and Contraction in Solids, Liquids and Gases Some materials expand on heating and some contract on cooling. Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of atomic motion.
Heat energy Most of us use the word ‘heat’ to mean something that feels warm, but science defines heat as the flow of energy from a warm object to a cooler object. The following sentences may answer your question:. Thermal energy is the internal energy of an object due to the kinetic energy of its atoms and/or molecules.
Thermal energy is used to warm the surroundings. Thermal Energy – Definition. The thermal characteristic test showed that with the increase of EG content, the thermal conductivity of the composite PCMs increased while the latent heat slightly decreased.
Actually, heat energy is all around us – in. Heat transfer is thermal energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a temperature difference. Thermal energy is what we call energy that comes from the temperature of matter.
ΔU isolated system = 0. Learn thermal energy with free interactive flashcards. A whole branch of physics, thermodynamics, deals with how heat is transferred between different systems and how work is done in the process (see the 1ˢᵗ law of thermodynamics ).
Kinetic energy is the energy associated with the movement of objects. You generate heat and have thermal energy with respect to your environment. Thermal energy is used to cook food.
Define conduction, convection, and radiation 2. Temperature is the measurable (macroscopic) property or state of the system. The geothermal energy of the Earth's crust originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials (in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions).
More simply put, heat energy, also called thermal energy or simply heat, is transferred from one location to another by particles bouncing into each other. For the composite PCM with 4 wt% EG, the thermal conductivity was increased by about 2.5 times and the latent heat was only decreased by 2.59% compared with that of the pure erythritol. A molecular picture of heat conduction will help justify the equation that describes it.
But the equation involves not T itself but the change in T during the energy-input process. Thermal energy is used to generate electricity. This includes wood and wood byproducts, municipal waste, methane from landfills, and fuel from agricultural crops.
2 Chapter 3 Thermal Energy perature, and E t for thermal energy. An isolated system cannot exchange heat or work with its surroundings making the change in internal energy equal to zero. For example, in the case of a diamond, the Eg is about 5.5eV, whereas the energy electron possesses at room temperature is 0.025eV.
The double-layered core is made up of very hot molten iron surrounding a solid iron center. Explain how thermal energy moves from one place to another Use this video with Educanon or Edpuzzle to make it more engaging for. Thermal Energy – Definition.
Energy entering the system is POSITIVE (+), meaning heat. It is one of the different types of energy, where energy basically refers to the ability to do work. Thermal energy (also called heat energy) is produced when a rise in temperature causes atoms and molecules to move faster and collide with each other.
The different types of energy include thermal energy, radiant energy, chemical energy , nuclear energy, electrical energy , motion energy, sound. Thermal energy is the cause for the temperature of a system. Heat energy is all around us such as in icebergs, volcanoes, and our bodies.
Types of energy can be categorised into two broad categories – kinetic energy (the energy of moving objects) and potential energy (energy that is stored). Heat (Thermal energy) Matter is made up of particles or molecules. It is also called thermal energy.
(Opens a modal) Work/energy problem with friction (Opens a modal) Conservative forces (Opens a modal). Every system having a temperature above absolute zero has a positive thermal energy. Although there are many forms of kinetic energy, this type of energy is often associated with the movement of larger objects.
Spring potential energy example (mistake in math) (Opens a modal) LOL diagrams (Opens a modal) Vertical springs and energy conservation (Opens a modal) Mechanical advantage. Thermal energy definition is the manifestation of energy in the form of heat. The atoms and/or molecules of a hotter object have greater kinetic energy than those of a colder one, in the form of vibrational, rotational, or, in the case of a gas, translational motion.
6 min, 47 sec. This reaction results in new chemical bonds of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and water. People around the world use geothermal energy to produce electricity, to heat buildings and greenhouses, and for other purposes.
A renewable energy source consisting of non-fossil biological material. The first law of thermodynamics. Thermal energy is energy possessed by a body or system due to the movement of particles within the body or the system.
We get electrical generators. These electric generators are run by hydropower, thermal power or nuclear power. (the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact.
ΔU system = -ΔU surroundings. Heat or thermal energy.
Thermal Energy Storage Wikipedia

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics

Photo To Thermal Conversion And Energy Storage Of Lauric Acid Expanded Graphite Composite Phase Change Materials Int J Energy Res X Mol

8 Thermal Expansion Examples Gcsephysicsninja Com

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between

Heat Transfer
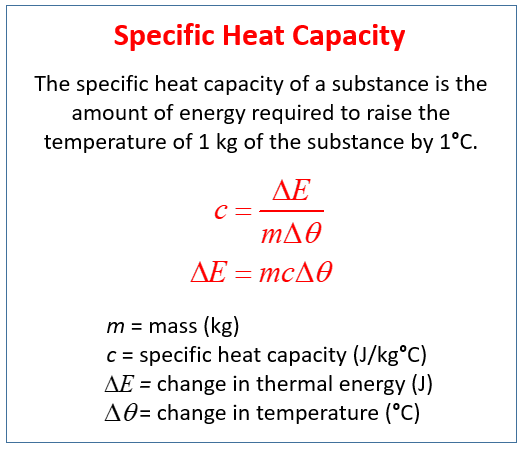
Specific Heat Capacity Examples Solutions Videos Notes

Thermal Conductors And Insulators Read Physics Ck 12 Foundation

Heat Wikipedia

Examples Of Heat Energy

Working Principle Ocean Thermal Energy Surface Water Warmer Than Deep Water Vapourise Low Bo Thermal Energy Energy Technology Renewable Energy Technology

Photovoltaic Thermal Hybrid Solar Collector Wikipedia
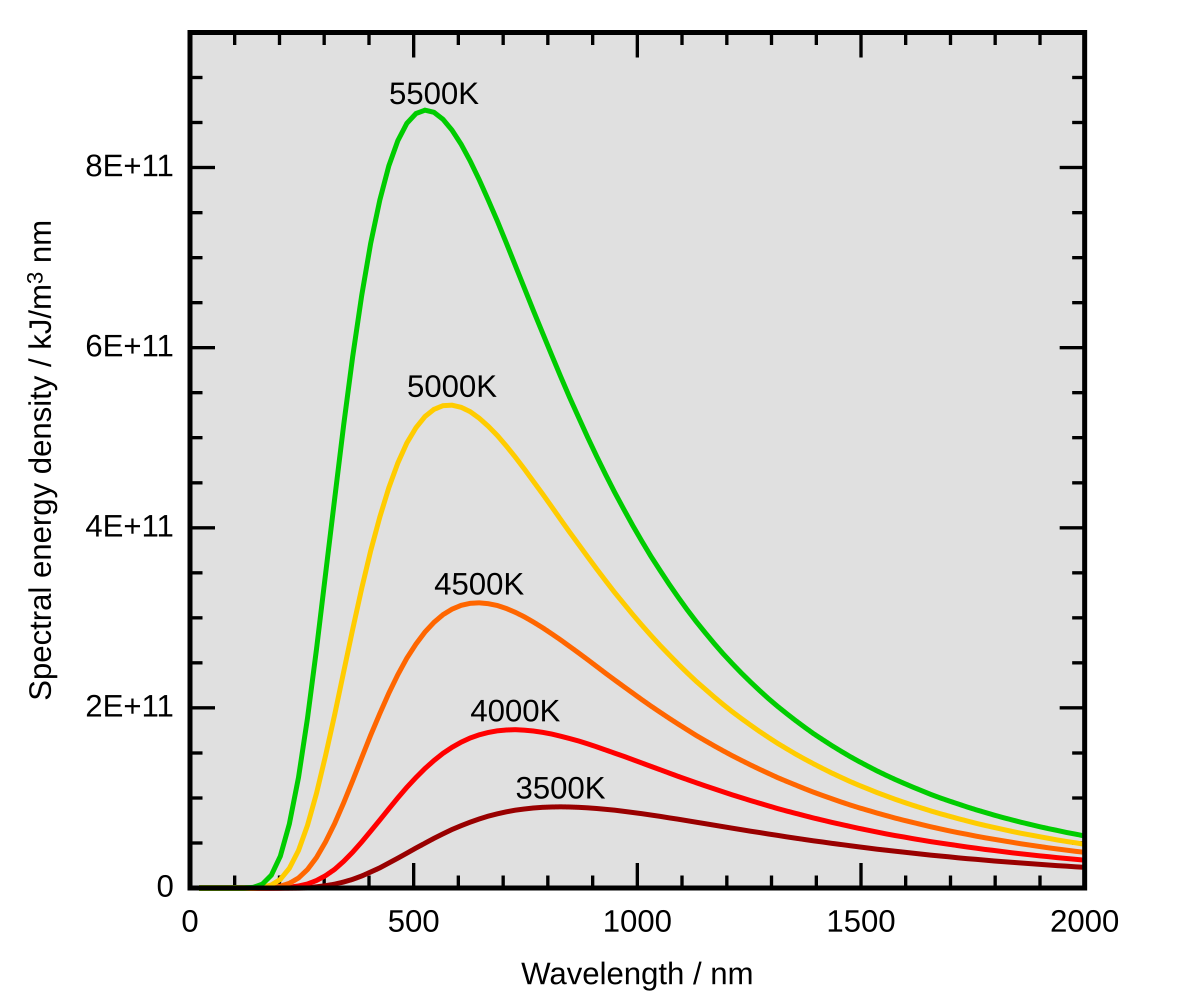
Thermal Radiation Wikipedia

Thermal Energy Storage Wikipedia

Heating As A Transfer Of Energy Heat Energy Transfer Siyavula

Block3 Html

Cogeneration Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqjcksjgfatid8dexgjp4njdhbv7zbqvscccglvdblxa Jdktk Usqp Cau

Kinetic Energy Examples

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Makai Ocean Engineering

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between
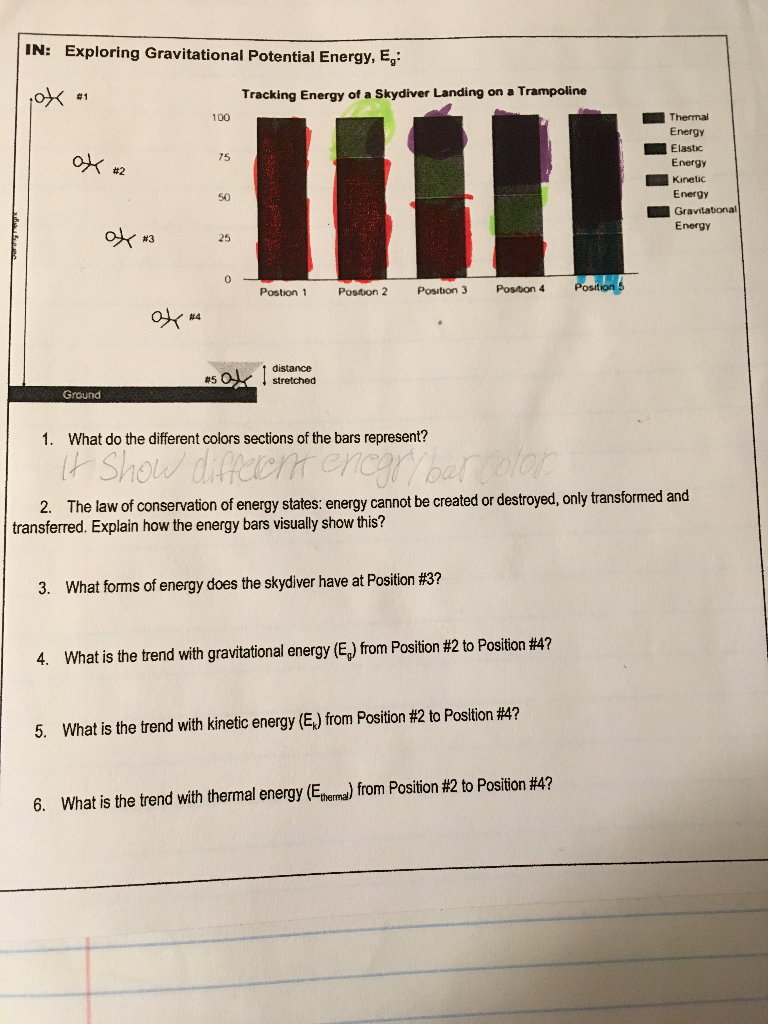
Solved 4 What Is The Trend With Gravitational Energy Eg Chegg Com

Flow And Thermal Energy Measurements In The Beer Brewing Process Flexim
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/close-up-of-food-boiling-in-utensil-at-kitchen-932522934-5bd9cd54c9e77c0051c40090.jpg)
What Is Latent Heat Definition And Examples
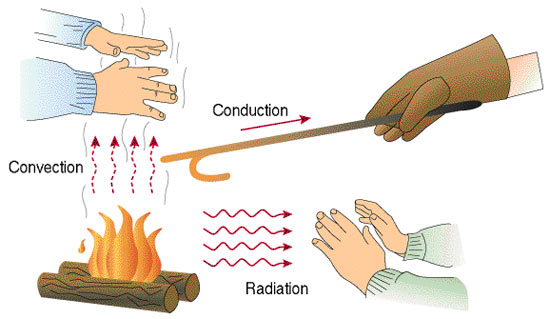
Heat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Videos And Case Study

What Is Thermal Energy Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Transfer Of Thermal Energy

Energy Kinetic Energy Energy In The Form Of Motion Individual Motion E G Batted Baseball Thermal Energy Energy Of Particles In Random Motion Potential Ppt Download

Benefits Of Thermal Energy Storage Nexant
Thermodynamics What Is The Difference Between Heat And Thermal Energy Quora
Energy And Work

What Is Thermal Energy Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Solved Thermal Energy Storage Tank A Tank Is To Be Used T Chegg Com

Schematic Of Rgo Eg Fluids For Direct Absorption Solar Thermal Energy Download Scientific Diagram

12 Examples Of Thermal Energy In Everyday Life Rankred
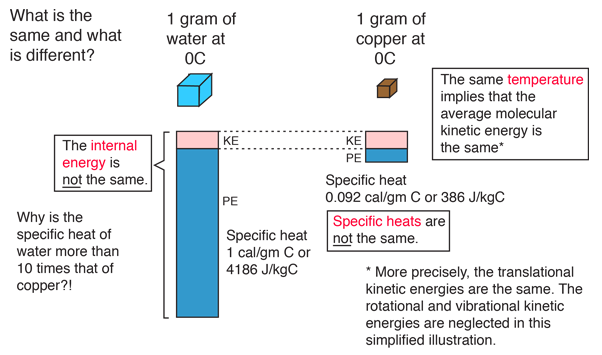
Internal Energy
1

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion U S Energy Information Administration Eia
/main-energy-forms-and-examples-609254-v3-5b562a0cc9e77c0037514831.png)
10 Types Of Energy And Examples

Heat Thermal Energy Ch 16 State Indicator 17 Demonstrate That Thermal Energy Can Be Transferred By Conduction Convection Or Radiation E G Through Ppt Download

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Makai Ocean Engineering

Thermodynamics Definition Laws Live Science

Thermal Energy Wikipedia

What Are Phase Change Materials Will They Be The Next Big Thing In Norway Sintefblog

About Heat Energy Heatcalc

What Is Thermal Energy Article Khan Academy

Potential Energy Definition Examples Facts Britannica

Pdf Synthesis Thermal Energy Storage Properties And Thermal Reliability Of Some Fatty Acid Esters With Glycerol As Novel Solid Liquid Phase Change Materials Ali Karaipekli Academia Edu

Effect Of Nano Sic On Thermal Properties Of Expanded Graphite 1 Octadecanol Composite Materials For Thermal Energy Storage Powder Technol X Mol
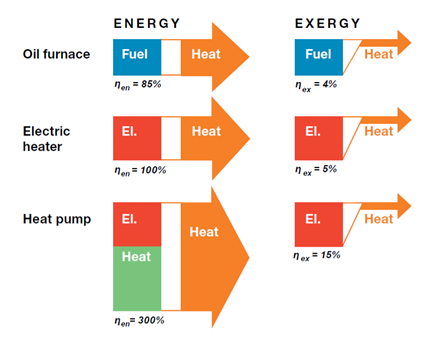
What Is Exergy Exergy Economics

Temperature Change And Heat Capacity Physics

Review Of Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage For Improved Material Stability And Effective Load Management Sciencedirect
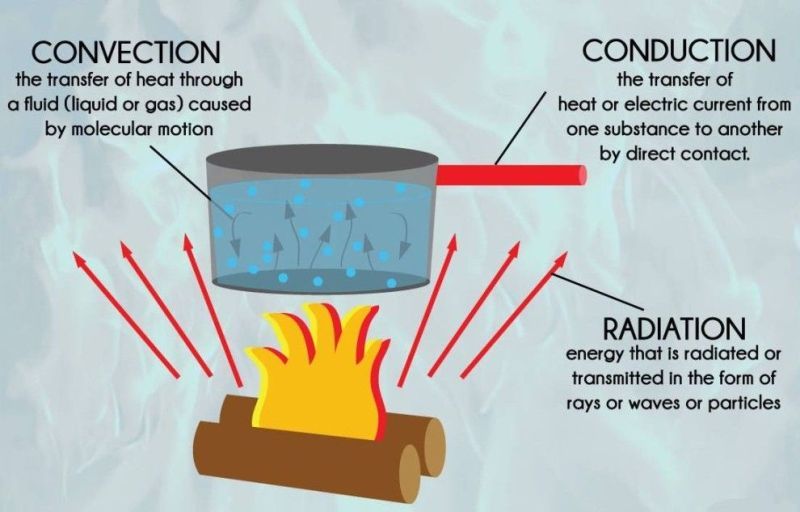
13 Examples Of Convection In Everyday Life Studiousguy

Central Campus Thermal Energy Connection Packages E G Building Bama The University Of Alabama

Pdf Thermal Energy Storage In Phase Change Materials Applications Advantages And Disadvantages

Examples Of Mechanical Energy At Home And In Daily Life
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrzad9oanwfqktbzkwy0ixywj2flyzzun13uvk98hqgphzgni D Usqp Cau

Energy Wikipedia

Energy Loss Energy Education

Heat Energy Definition Sources Of Heat Energy And Examples

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Wikipedia
3

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Technology Britannica
Q Tbn 3aand9gctkvwe7njjwivgfsdiq Z36b6uory3698oqfa Usqp Cau

Heat Transfer Thermal Insulation Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Overview Objective Background Materials Procedure Report Presentation Closing Objectives Design

What Is Heat Definition Explanation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Energy Transformation Wikipedia

What Is Thermal Energy Article Khan Academy

What Is Thermal Energy Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Www Lcps Org Cms Lib Va Centricity Domain 3318 Thermal energy Pdf

Solved Thermal Energy Storage Tank A Tank Is To Be Used T Chegg Com
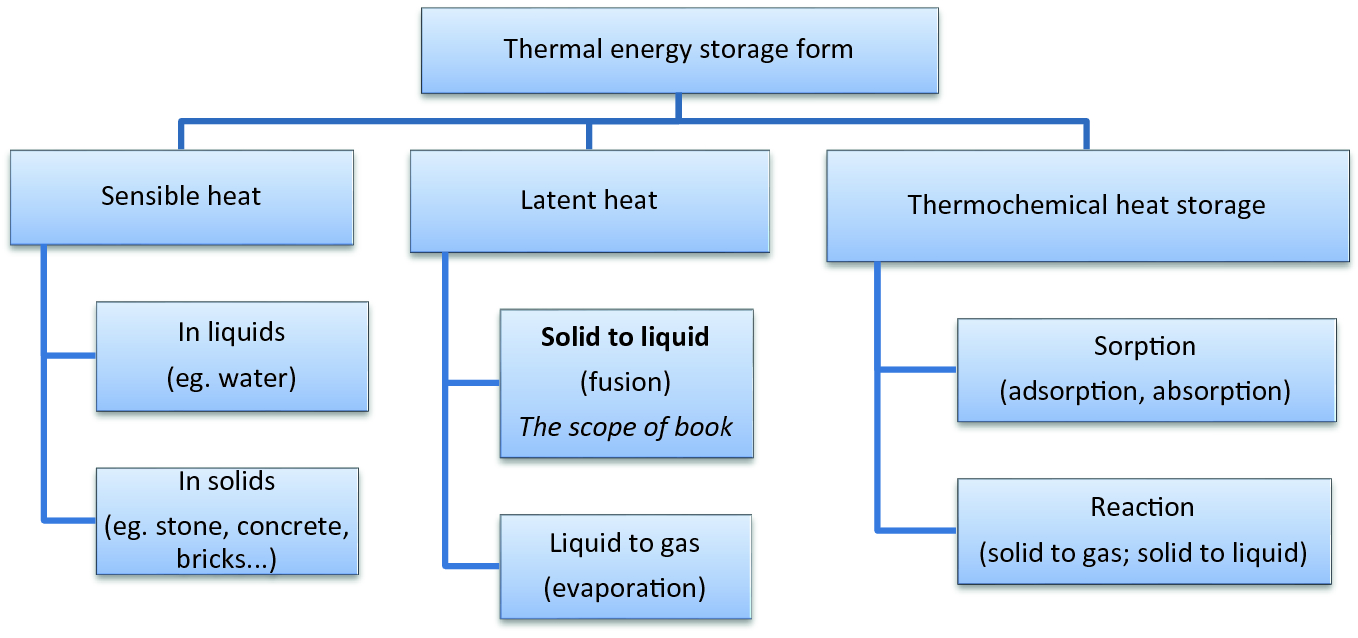
Introduction Springerlink
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqfywmzzvdig7qwtdwpeziwqfrzjrns6nega Usqp Cau

Thermal Energy Storage Recent Developments And Practical Aspects Sciencedirect

Chp For Hospitals Superior Energy For Superior Patient Care Combined Heat And Power Chp Partnership Us Epa
Transfer Of Thermal Energy

Heat Is Transferred 3 Ways Ppt Video Online Download

Flow And Thermal Energy Measurements In The Beer Brewing Process Flexim

What Is The First Law Of Thermodynamics Article Khan Academy

Thermal Energy Storage Recent Developments And Practical Aspects Sciencedirect
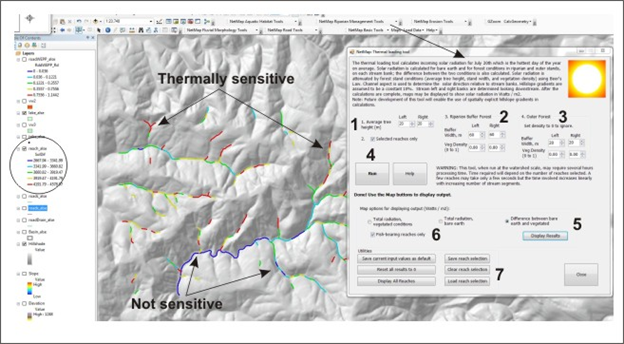
Topic Thermal Energy Sensitivity
/heat-energy-definition-and-examples-2698981-final-2-5b76efbcc9e77c005028d736.png)
Definition And Examples Of Heat Energy

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics

Forms Of Energy Transformations Of Energy And Their Real World Applications

Sustainability Free Full Text A Comprehensive Review Of Thermal Energy Storage Html

Thermal Energy Transfer Pbs Learningmedia
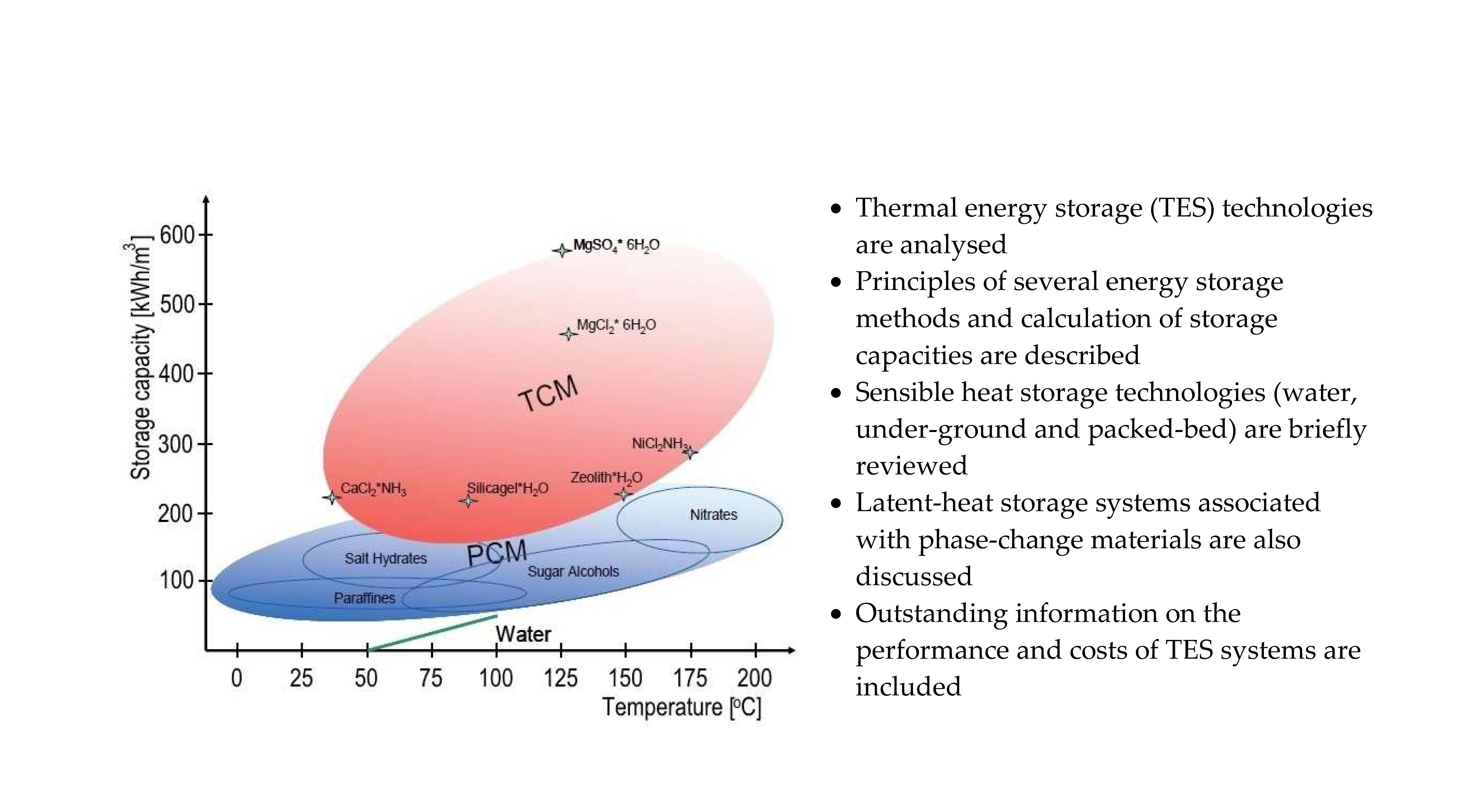
Sustainability Free Full Text A Comprehensive Review Of Thermal Energy Storage Html

5 1 The Nature Of Energy Chemistry Libretexts

About Heat Energy Heatcalc

What Is Thermal Energy Article Khan Academy

Columbia Sipa Center On Global Energy Policy Low Carbon Heat Solutions For Heavy Industry Sources Options And Costs Today
Energy Types Of Energy Young People S Trust For The Environment
Www Flippedoutscience Com Uploads 2 7 8 2 Energy Transformations Notes Pdf
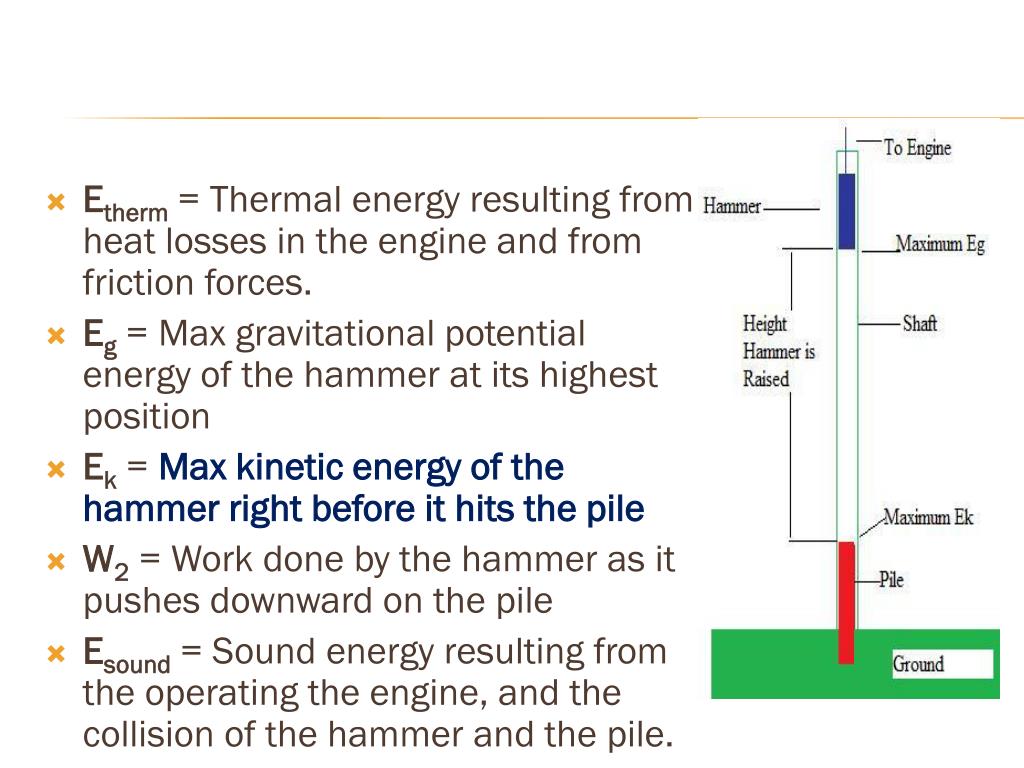
Ppt Thermal Energy And Heat Conservation Of Energy Powerpoint Presentation Id

Ppt Notes 22 Topic 3 Thermal Physics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Thermal Energy Bandgap Of Antimony Trisulphide At 300k Download Scientific Diagram

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between

Wisconsin Online Heat Transfer Pbs Learningmedia



