Eg Of Heat Energy
Energy Transformation Wikipedia

Thermodynamics Definition Laws Live Science
/heat-energy-definition-and-examples-2698981-final-2-5b76efbcc9e77c005028d736.png)
Definition And Examples Of Heat Energy
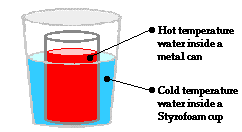
The Physics Classroom Tutorial

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics
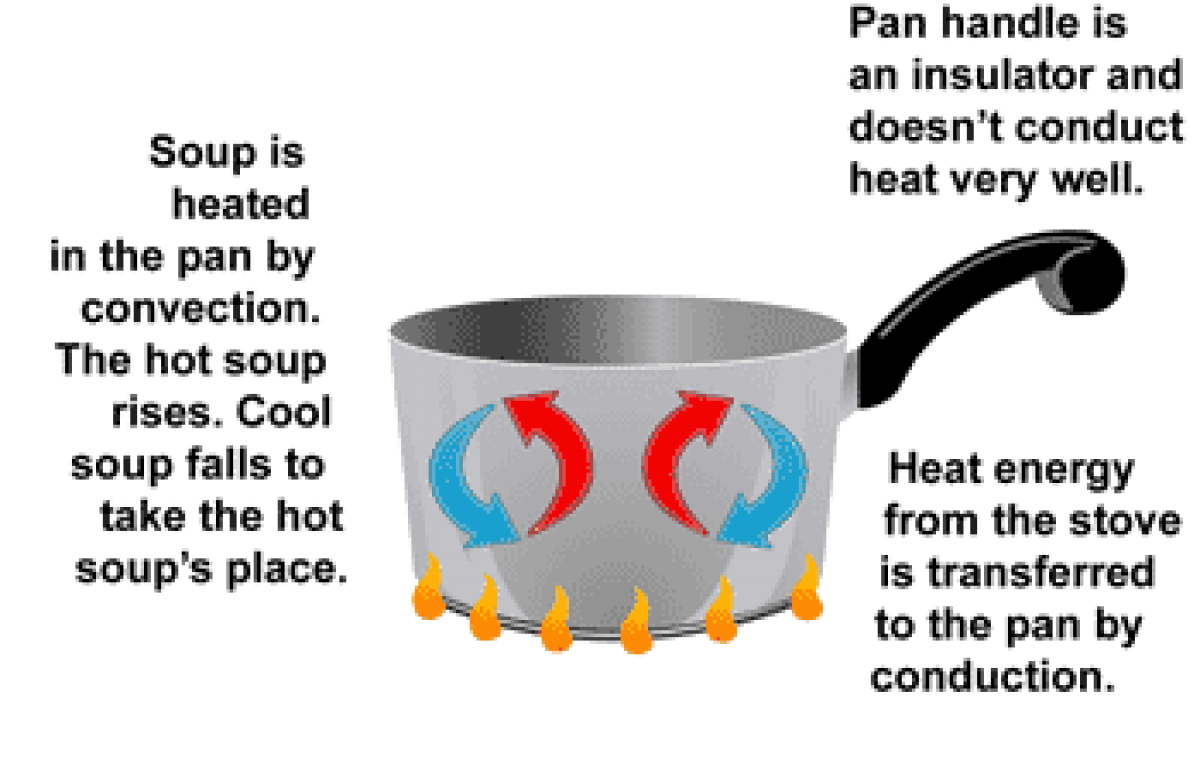
The Importance Of Good And Bad Conductors Of Heat Science Online
The following sentences may answer your question:.

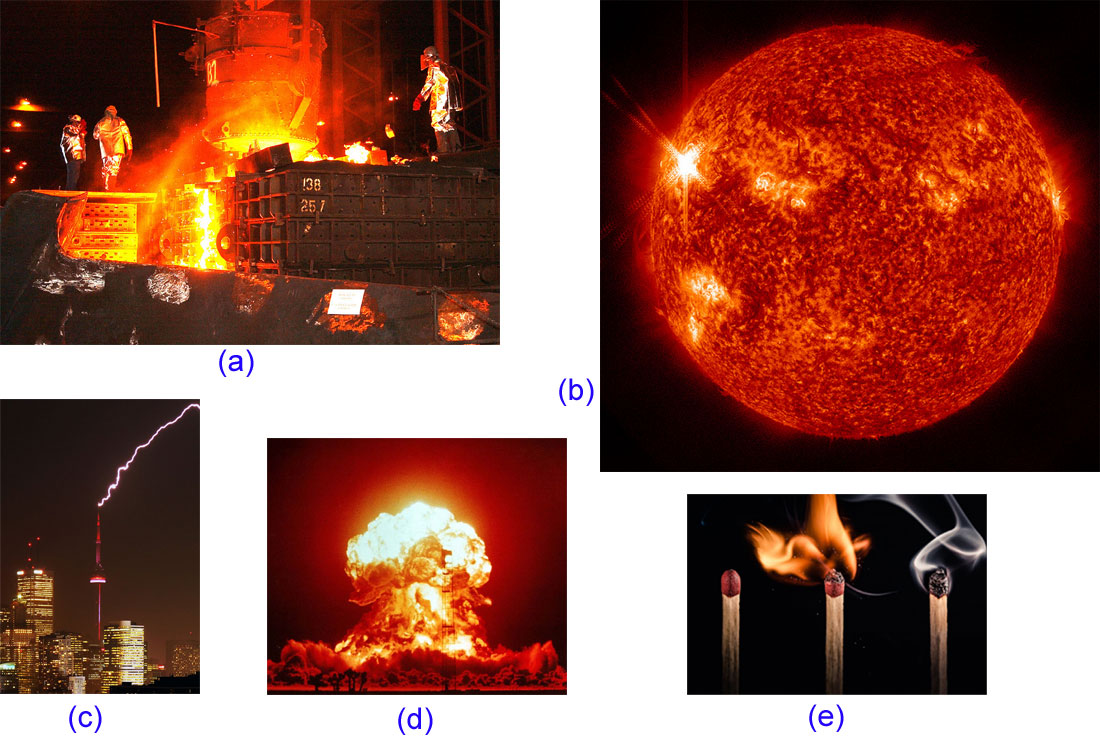
Eg of heat energy. Get comprehensive coverage of your oil heat system with our Premier Plan, which includes our 24-hour “No Charge” parts and labor coverage. The more movement, the more. The biggest example of heat energy in our solar system is the sun itself.
It can be expressed as the following formula:. Energy Transformations see diagram…. The main feature of heat is that it travels from hotter region to cooler region.
This chapter is on the tran. C Specific heat of water 4.184 kJ/kg. Cp = cv (1) The specific heat represents the amount of energy required to raise 1 kg of substance by 1oC (or 1 K), and can be thought of as the ability to absorb heat.
These are safe, abundant, and clean to use when compared to fossil fuels which are non-renewable energy. Heat transfer is thermal energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a temperature difference. To absorbing light energy and heat energy.
• Heat rate is a measure of the amount of energy required to generate a unit of electricity. Most people simply refer to thermal energy as heat. Heat energy Most of us use the word ‘heat’ to mean something that feels warm, but science defines heat as the flow of energy from a warm object to a cooler object.
Those statements all mean the same thing. Heat, energy that is transferred from one body to another as the result of a difference in temperature. The SI units of specific heats are J/kgK (kJ/kgoC).
Geothermal energy uses heat from the interior of the Earth. Thermal energy is used to warm the surroundings. Energy is required for the evolution of life forms on earth.
Or try our Comfort Plan — a value-priced option. A blanket of CO2 blocks radiation into space and makes a global green house, ie the Earth has to get hotter in order to re-radiate the sun's input. Hot coalsWalking on hot coals is a good example of the difference between temperature and heat.
The fluid in the tubes absorbs the heat from the ground so it can be used to heat your home and water. Power plants and internal combustion engines are examples of heat engines. A great deal of heat energy comes from the Sun's light hitting Earth.
Heat measures both kinetic and potential energy contained by molecules in an object. Some heat is generated by the Earth's core so energy radiated into space is a bit more than the sun's input. The thermal energy of every matter will always depend on the speed.
A waterfalls is 90m high. Heat energy is all around us such as in icebergs, volcanoes, and our bodies. Heat Pipes, Agitated Vessels and Graphite Block Exchangers can be regarded as tubular or could be placed under Recuperative "Specials".
More simply put, heat energy, also called thermal energy or simply heat, is transferred from one location to another by particles bouncing into each other. If two bodies at different temperatures are brought together, energy is transferred—i.e., heat flows—from the hotter body to the colder. One of the most important types of energy on Earth is heat energy.
It quickly changes into different forms of energy like light, electricity, etc. = 5 × 40 × 100. Thermal energy is used to cook food.
Using energy balance relations, ie., increase of stored energy in a volume of material = energy in + energy generation in this volume - energy out, we can deduce the general differential form of three dimensional heat conduction equation. The fans heard whirring in computers are designed to remove heat generated by the electronics. Heat Energy Most of us refer the word ‘heat’ to anything that feels warm but scientifically, heat is defined as the flow of energy from a warm to a cooler object.
In the process, the light energy converts to heat energy. Mechanical energy into heat energy. A cup of hot coffee has thermal energy.
Renewable Sources of Energy Advantages:. Thermal energy is one of various types of energy, where ' energy ' can be. Thermal energy or heat energy reflects the temperature difference between two systems.
An ice cube will soon melt if you hold it in your hand. Heat energy, also called thermal energy, is the energy an object has because of the movement of its molecules, and heat can be transferred from. With each plan, you get lower energy costs, longer equipment life, and peace of mind.
This does not harm the planet. The crossword clue possible answer is available in 5 letters.This answers first letter of which starts with T and can be found at the end of M. We also offer a money-saving Water Heater Coverage Plan.
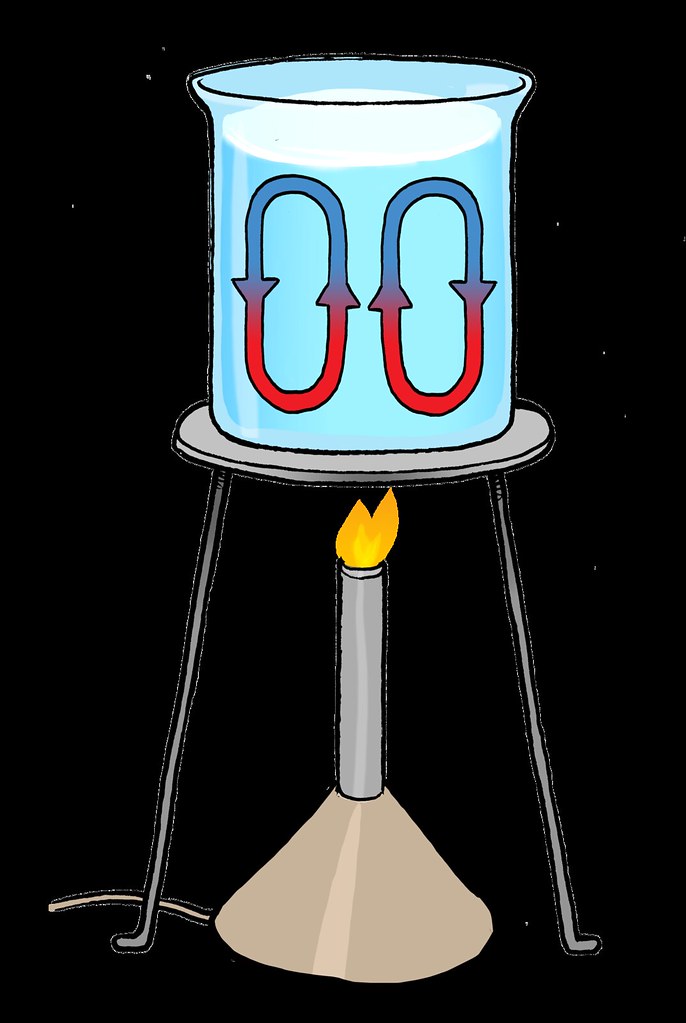
In this lab, we will focus on the ways heat is transferred. C Heat of dissolution of PTA 472 kJ/kg. Mechanical work is done when a force f displaces an object by a distance d:.
This unit helps students understand what heat energy is, how it is transferred, how it is measured, and how insulation. This energy will not be recoverable if the process is reversed. The classification of heat is done on this basis as hot and cold.
For solids and liquids. We know that energy exists in different forms in nature. Fossil fuels used in the combustion of fossil fuels (for instance, heat engines).
Solar energy enters our atmosphere as shortwave radiation in the form of ultraviolet (UV) rays (the ones that give us sunburn) and visible light. The sun emits shortwave radiation because it is extremely hot and has a lot of energy to give off. Thus the heat energy given off by the hot liquid is equal to the heat energy absorbed by the cold liquid, i.e.
This ScienceStruck post discusses the methods of heat transfer and its applications in detail. Heat is a shortened way of saying "heat energy." When something's hot, it has a lot of heat energy;. Heating systems use convection heat transfer in order to get warm air.
The man knew about heat and its precursor fire for ages and had been using it for various applications. Quantity of heat energy, Q = mc ( t 2 – t 1) = 5 kg × 40 J/ (kg °C) × (100 – 0)°C. Heat of EG 2.42 kJ/kg.
Potential energy is energy that is stored in an object or substance. The distinction between heat and temperature is not important for your elementary students. The sun radiates heat to warm us up on the planet earth.
When the burner of a stovetop is very hot, it is a source of heat energy. Assume the specific heat capacity of water is 40 J/ (kg °C). There are different types of energy, such as heat energy, mechanical energy, light energy, sound energy and electric energy.
This crossword clue Heat energy unit was discovered last seen in the June 7 at the Premier Sunday Crossword. Its usage existed even before petroleum and nuclear power sources were discovered. A heat pipe consists of a pipe, a wick material and a working fluid.
However, in many applied fields in engineering the British thermal unit (BTU) and the calorie are often used. Unlike temperature, which rises when heated and falls when cooled. The heat is used to increase the thermal energy of a metal which melts and is used to weld pipes together.
This energy causes the thermal energy of the solution inside the bag to increase and we feel heat to warm our hands. Renewable Sources of Energy Disadvantages:. During this transformation, there will be some heat energy loss or dissipation due to intermolecular friction and collisions.
C Heat of vaporization of water at(285 C) 1439 kJ/kg. This energy source is stable. Since the air is a fluid, differences in temperature favor convection;.
Ground basis heat pumps can be fixed to connect the normal heat from underground using fluid tubes covered outside the assets. Anything placed onto the stovetop and warmed, whether a pot of tea or a skillet for frying eggs, also become sources of heat energy. Of heat - that mechanical energy could be transformed into heat and vice-versa - was a major achievement of 19th century physics.
Whenever two things of different temperatures are near one another, thermal energy flows. Heat is a form of energy. Heat transfer from a body with a high temperature to a body with a lower temperature, when bodies are not in direct physical contact with each other or when they are separated in space, is called heat radiation 1, as schematically shown in Fig.
Heat Capacities The amount of energy (heat) required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by 1 oC. Heat energy will flow in the direction from the tea to my hand (not vice versa). This flowing energy is called heat.
General equation of Heat Conduction:. Multiple forms of energy sources exist in nature. Heat is a form of energy that exists naturally.
You have learned about various forms of energy – heat, electrical, chemical, nuclear, etc. Assume that all of the potential energy possessed by the water at the top is completely converted to heat energy. Hot food will heat a stoneware or porcelain plate for a time.
• By employing a broad range of HRI technologies and techniques, EGUs can more efficiently generate electricity with less carbon intensity. The standard unit for the rate of heat transferred is the watt (W), defined as one joule per second. Thermal energy forms the foundation of the study of heat energy and thermodynamics.
This is low maintenance energy sources. Here are some examples of conversion of mechanical energy into heat energy. Thermal energy is energy possessed by an object or system due to the movement of particles within the object or the system.
Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of atomic motion. Constant-volume and constant-pressure heats can be said to be equal. Chemical energy of butane is converted to heat.
Heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g K = 1 calorie 1) Heat capacity is dependent on heat Eg. As the name suggests, heat transfer is the travel of heat or thermal energy from one object or entity to another. Thermal Energy This effort was closely tied to the industrial revolution and the need to understand how things like steam engines (which convert heat into mechanical energy) work É Read Chapter 7.
You generate heat and have thermal energy with respect to your environment. In this article, we will learn about the laws and principles that govern energy. Notice that these energy transfer examples only show the useful energy transfers.
The working fluid absorbs heat, evaporates and passes to the other end of the heat pipe were it condenses and releases heat. Other sources include geothermal energy, friction, and even living things. (i) When wood or coal is burnt in the hearth, heat is produced first and then light.
The heat is being conducted from your hand into the ice cube. The faster the atoms are moving, the higher the temperature. .000 l/h cheese milk (V 1) is to be heated from 4 °C to 34 °C by 30.000 l/h hot water (V 2) at 50 °C.
Both heat and light energies are so closely related that the presence of one calls in the other. Most of us take heat, a form of energy, for granted!. The suns energy heats the earth until a balance is reached.
It is one of the oldest forms of energy utilized by mankind. In physics, it is defined as the capacity to do work. C Heat of vaporization of EG at (285 C) 573 kJ/kg.
Hot air rises and cold air down. Calculate the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 5 kg of water from 0°C to 100°C. This liquid conducts heat energy very efficiently.
When it's cold, it has less. 3.1.All physical substances in solid, liquid, or gaseous states can emit energy via a process of electromagnetic radiation because of vibrational and. Heat energy is produced when there is a transfer of heat from a warm object to a cool object.
• An improvement to heat rate results in a reduction in the emission rate of an EGU (in terms of CO. C PET Actual operating condition. Heat is the flow of thermal energy that arises from temperature differences.
Heat energy can be transferred from one object to another. All matter contains heat energy, and the more heat energy that is present, the hotter an item or area will be. On the other hand, temperature measures average kinetic energy of molecules in substance.
The Law of Conservation of energy is that energy can be transformed from one form to another, but can be neither created or destroyed. Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. 10 oC o 11 oC and 80 oC o 81 oC, require slightly different energies.
This transfer takes place in three ways - conduction, convection, and radiation. We think of calories as just things that are in food and all foods have calories. A butane torch burns butane gas.
As a form of energy, heat has the unit joule (J) in the International System of Units (SI). The transfer or flow due to the difference in temperature between the two objects is called heat. Hotter things have more heat energy than colder things.
Heat energy turns ice into steam. As the chemical bonds are broken during the reaction, heat is released. Life on this earth depends on heat energy for survival.
The engine absorbs heat Q h Q h from a heat source (hot reservoir) of Kelvin temperature T h, T h, uses some of that energy to produce useful work W, and then discards the remaining energy as heat Q c Q c into a heat sink (cold reservoir) of Kelvin temperature T c. But your body sees calories as energy and it's energy. What will be the temperature difference between the water.
The heat from a hot liquid makes the cup itself hot. A calorie is actually a unit of heat energy. (1) w = f × d The basic unit of energy is the joule.
C Specific heat of oilgomer CP4 esterification system works under steady state 2.09 kJ/kg. Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms, molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. = J or 2100 kJ or 2.1 MJ.
If you are cold and someone holds you to warm you, the heat is being conducted from their body to yours. This is an important form of energy as it is essential for day-to-day activities like cooking, ironing and the heating of water. But even things that seem cold (such as polar bears and icebergs) have rather more heat energy than you might suppose.
Once in the Earth’s atmosphere, clouds and the surface absorb the solar energy. Energy is measured in terms of its ability to perform work or to transfer heat. For assets that are located close to a river or lake, it is achievable to fix a heat pump for a.

Energy Transformation Wikipedia

What Is Radiation Mission To Mars

Convection Conduction And Radiation

Heat Wikipedia

5 1 The Nature Of Energy Chemistry Libretexts

Heat Transfer

Heat Transfer Methods Physics

Specific Heat Example Problem

Types Of Energy Different Forms Of Energy Physics Youtube

Transfer Of Heat Wikiversity

Heat Transfer Wikipedia

Heat Transfer 1

What Is Infrared Striking Energy

Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate

Refrigeration And Phase Changes

Heat Exchangers Dairy Processing Handbook

What S The Difference Between Conduction Convection And Radiation Machine Design

Thermal Conductors And Insulators Read Physics Ck 12 Foundation

12 Examples Of Thermal Energy In Everyday Life Rankred

Heat Transfer

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics

13 Examples Of Convection In Everyday Life Studiousguy

Forms Of Energy Transformations Of Energy And Their Real World Applications

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics

Block3 Html
3

Heat Transfer Definition Facts Britannica
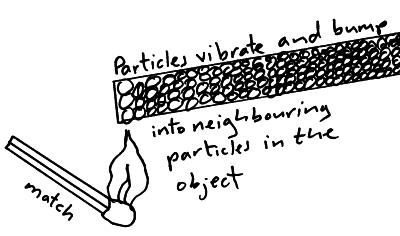
Energy Transfer By Heating Conduction Convection Evaporation Condensation

Examples Of Heat Conduction

When I Sit By A Campfire How Does Its Hot Air Heat Me Science Questions With Surprising Answers
Q Tbn 3aand9gctwktjo86ckzmvqwdf5t0lymjb746yl4bzof4jmgopdbdbdh6en Usqp Cau
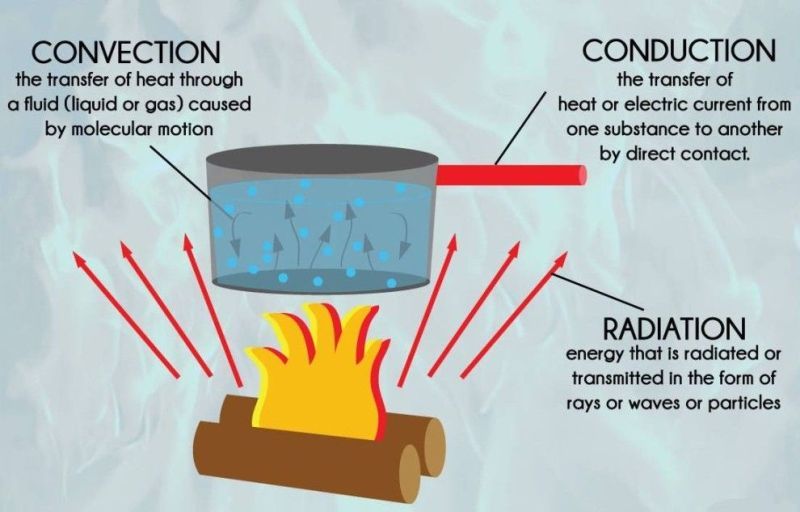
13 Examples Of Convection In Everyday Life Studiousguy
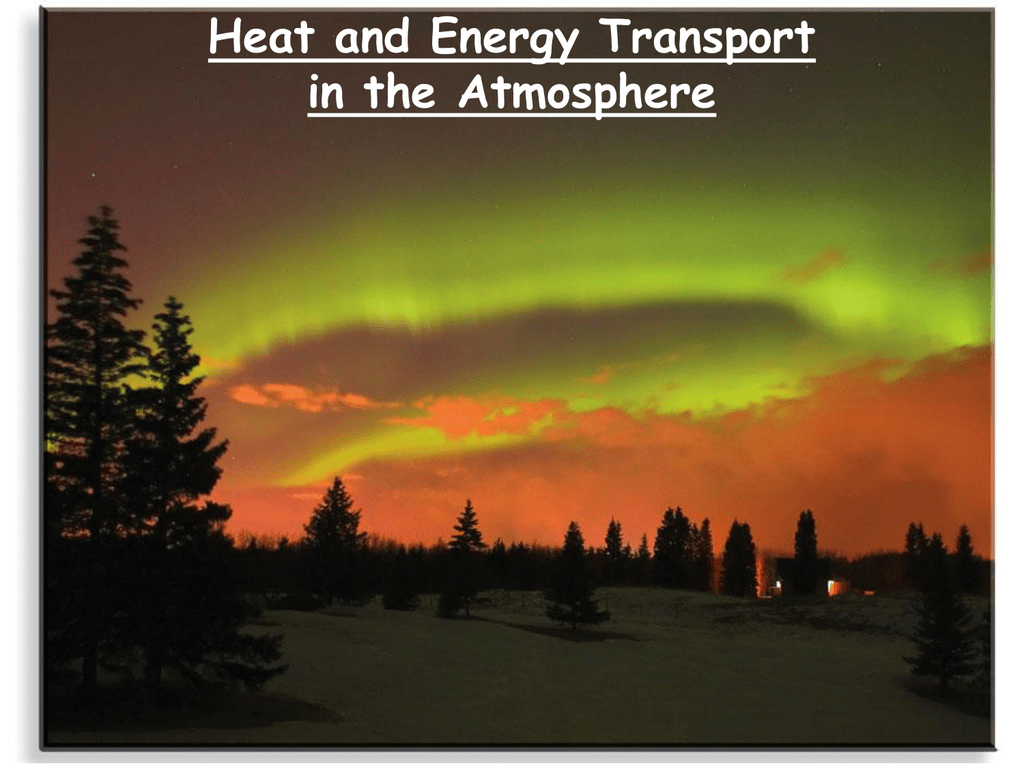
Heat And Energy Transport In The Atmosphere

Heat Transfer Thermal Insulation Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Overview Objective Background Materials Procedure Report Presentation Closing Objectives Design
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqfywmzzvdig7qwtdwpeziwqfrzjrns6nega Usqp Cau

Energy Loss Energy Education

Heat Engine Wikipedia

What Is Thermal Energy Article Khan Academy
1

Methods Of Heat Transfer Boundless Physics
What Are Some Examples Of Convection Heat Transfer Quora

Heat Transfer Definition Facts Britannica

What Is The First Law Of Thermodynamics Article Khan Academy

3 9 Energy And Chemical And Physical Change Chemistry Libretexts

Heat Transfer Through Popping Popcorn Perkins Elearning

What Is Thermal Energy Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Heat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Videos And Case Study

The Science Of Heat Transfer What Is Conduction Universe Today
Q Tbn 3aand9gctkvwe7njjwivgfsdiq Z36b6uory3698oqfa Usqp Cau

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between

Science For Kids Heat Energy Video Youtube

Types Of Heat Transfer Cooking Methods Examples

Examples Of Heat Energy
Thermodynamics What Is The Difference Between Heat And Thermal Energy Quora

The Physics Classroom Tutorial

Solved Question 1 The Rate Of Heat Energy Transfer 0 Chegg Com
/main-energy-forms-and-examples-609254-v3-5b562a0cc9e77c0037514831.png)
10 Types Of Energy And Examples

Convection Wikipedia
Www Lcps Org Cms Lib Va Centricity Domain 3318 Thermal energy Pdf

Temperature Change And Heat Capacity Physics

Examples Of Mechanical Energy At Home And In Daily Life

Heat Transfer By Thermal Convection Tec Science

The Energy Balance At Surface Net Radiation Sensible Heat Latent Heat Ground Heating 0 1 St Law Of Thermodynamics Conservation Of Energy Energy Ppt Download

Royal Heating Energy Efficiency Retrofit Of Historical Buildings Euroheat Power

Heat Transfer

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between
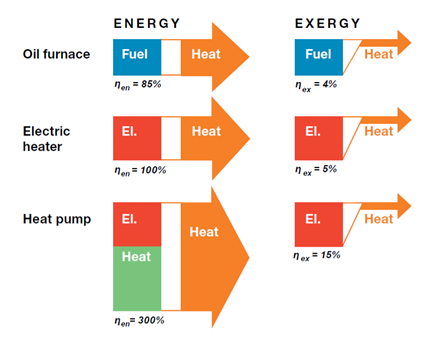
What Is Exergy Exergy Economics
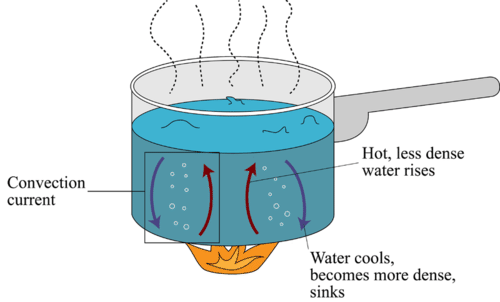
Convection Read Physics Ck 12 Foundation

Heat Transfer Medium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Energy And Work

Heat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Videos And Case Study

Heat Energy Definition Sources Of Heat Energy And Examples

Heat Transfer Through Conduction Equation Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

12 Examples Of Thermal Energy In Everyday Life Rankred
/xraysun-56a1296a5f9b58b7d0bca05e.jpg)
Examples Of Electromagnetic Energy
Energy Types Of Energy Young People S Trust For The Environment

What Is Heat Definition Explanation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Heat Transfer How Is Heat Transferred From One Place To Another What Is Moving In Mechanics Energy Can Be Transferred Through A Particle E G Ppt Download

How Does Heat Travel From The Sun Through Space Or Vacuum

Thermal Energy Storage Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrzad9oanwfqktbzkwy0ixywj2flyzzun13uvk98hqgphzgni D Usqp Cau
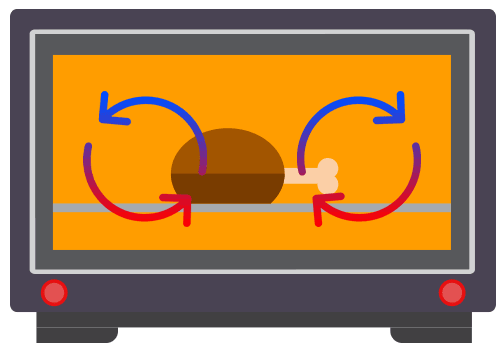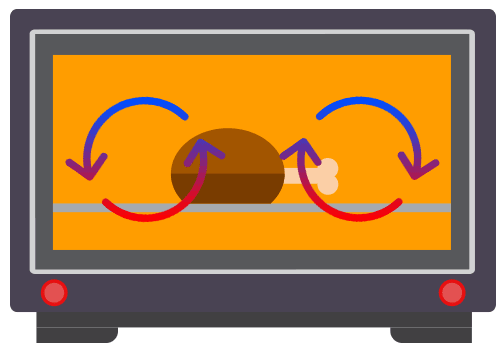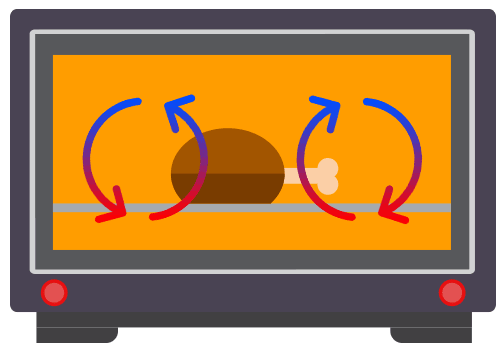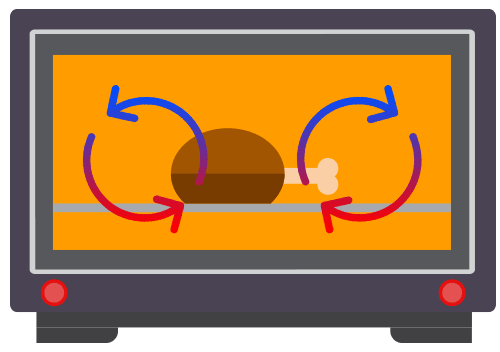
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrgqzdm0oukd0mv80 Pscmwv Uuuyunuerksq Usqp Cau

Columbia Sipa Center On Global Energy Policy Low Carbon Heat Solutions For Heavy Industry Sources Options And Costs Today

Heating As A Transfer Of Energy Heat Energy Transfer Siyavula

Thermal Energy Transfer Pbs Learningmedia

Conduction Ucar Center For Science Education
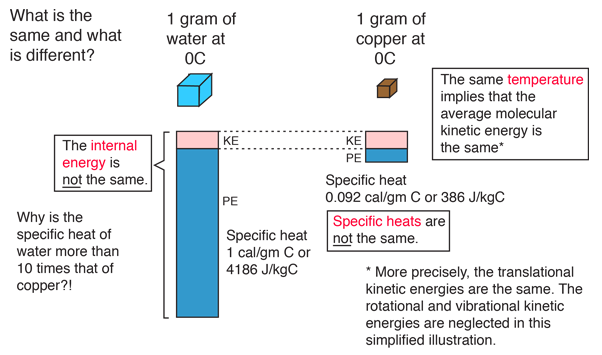
Internal Energy
Thermal Energy Storage Wikipedia

Kinetic Energy Examples
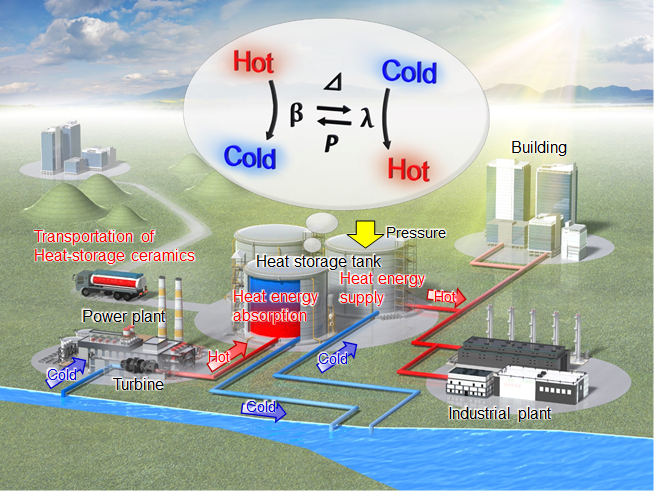
Development Of Long Term Heat Storage Ceramics Storing Waste Heat From Power Plants And Factories Through Hot Water School Of Science The University Of Tokyo

How Does Heat Travel From The Sun Through Space Or Vacuum

Heat Transfer By Thermal Convection Tec Science

Solved Identify The Point S On The Following Diagram Whe Chegg Com

The Electromagnetic Spectrum

Potential Energy Definition Examples Facts Britannica
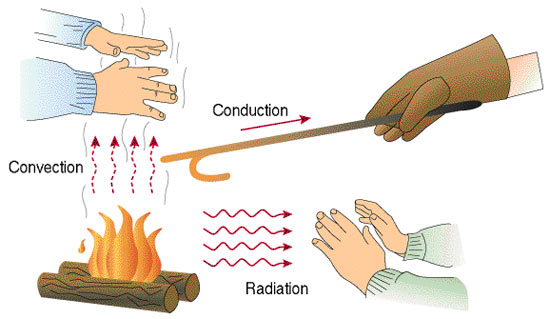
Heat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Videos And Case Study

Difference Between Temperature And Thermal Energy Difference Between

Eat Transfer Heat Transfer Thermal Conduction



